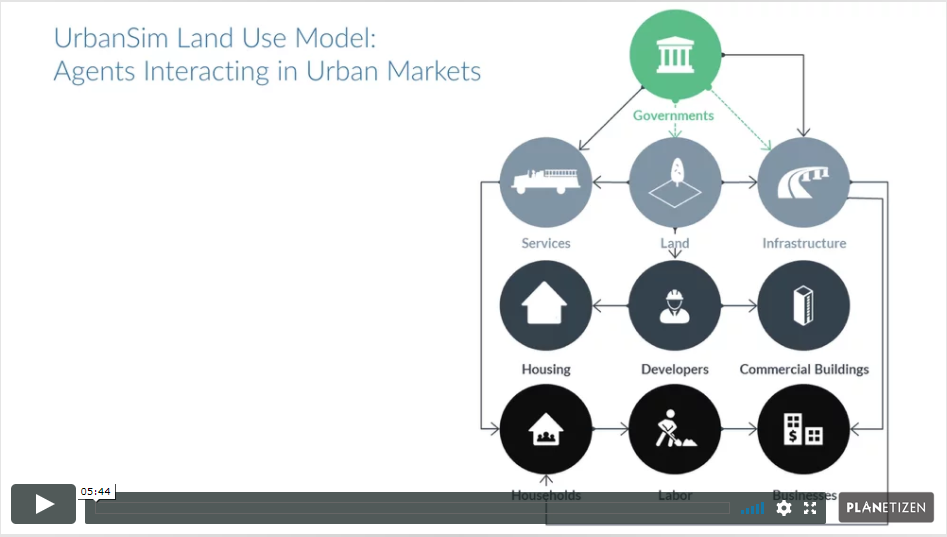
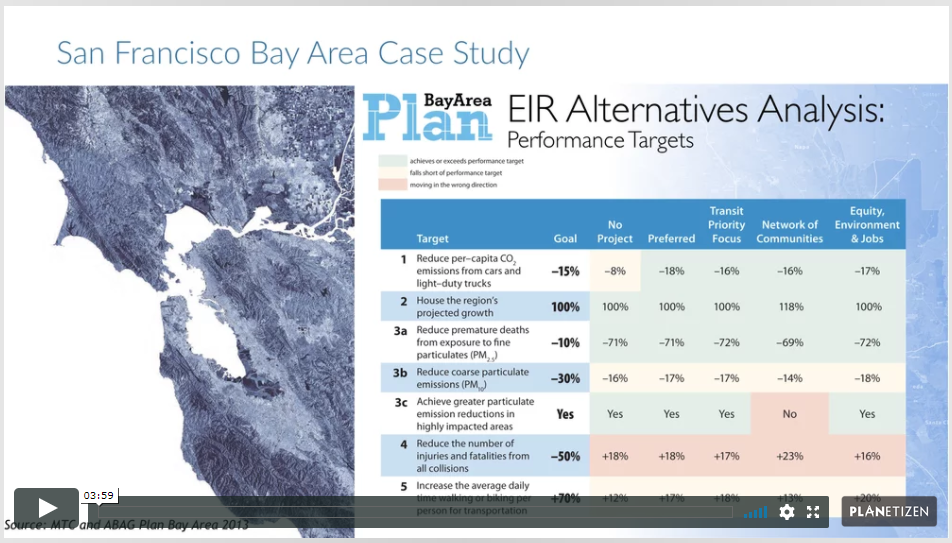
Workshops and Courses¶
Planetizen courses:
We have partnered with Planetizen to release two courses on UrbanCanvas Modeler that can count towards American Institute of Certified Planners Certification Maintenance (AICP CM) credits. Please note that Planetizen may no longer be offering these courses for free.
Note
The courses below show version v0.2.1 of the platform released in April 2017 and may not represent features currently included in the latest release.
Course 2: Regional Planning Workflows in the UrbanSim Cloud Platform
Course 1: Introduction to the UrbanSim Cloud Platform¶
Total time: 52 min
The UrbanSim Cloud Platform provides pre-built UrbanSim models and supporting tools for crafting and evaluating a socioeconomic forecast for a small geographic area.
At the end of this course, participants will be acquainted with the UrbanSim forecasting methodology, understanding the features available in UrbanCanvas and the basics of an UrbanSim model at the Census block level.
We will develop familiarity with UrbanCanvas’s user interface and explore how to use the platform to track a city’s development pipeline, edit development and zoning constraints, and refine a forecast. We will use the platform to compose scenarios, launch UrbanSim simulations, and visualize model outputs using the 3D mapping interface.
1. Introduction (3 min)
Introduction to the course.
2. Land Use Forecasting and UrbanSim (5 min)
Learn about the role of land use forecasting and UrbanSim in regional planning. This chapter also discusses the open-source tools and community behind UrbanSim.
3. UrbanSim Methodology (6 min)
Learn about the theoretical basis and the design of UrbanSim.
4. UrbanSim Case Studies (4 min)
Learn the common policy evaluation use cases for UrbanSim.
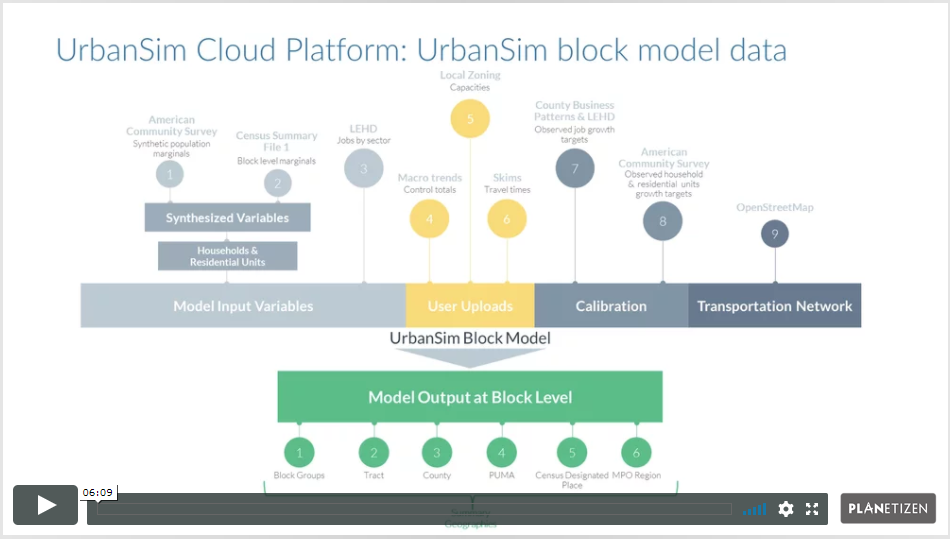
5. UrbanSim Model Templates (7 min)
Learn about the differences between the three UrbanSim model templates, the data schema of the block-level model, and the recommended UrbanSim model development path.
6. UrbanSim Cloud Platform Overview (4 min)
Develop familiarity with UrbanCanvas and its user interface. This chapter gives a tour of the platform’s menus, toolbar, and map navigation.
7. Running Your First Simulation (5 min)
In this chapter, we run a simple simulation to illustrate the platform’s capabilities.
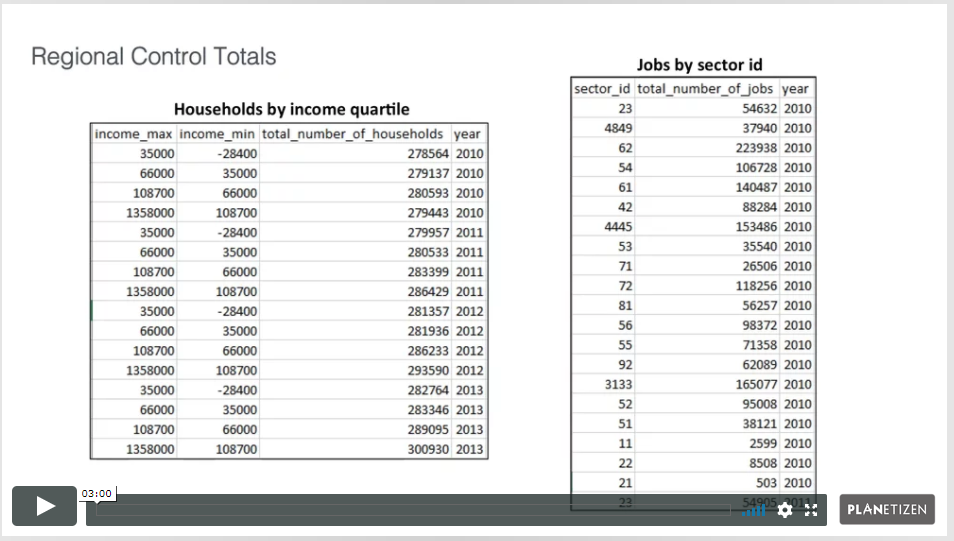
8. Uploading Data (3 min)
Learn about the data categories that can be uploaded into the UrbanSim platform. This chapter also shows how to upload local data to the platform to supplement the core behavioral simulation.
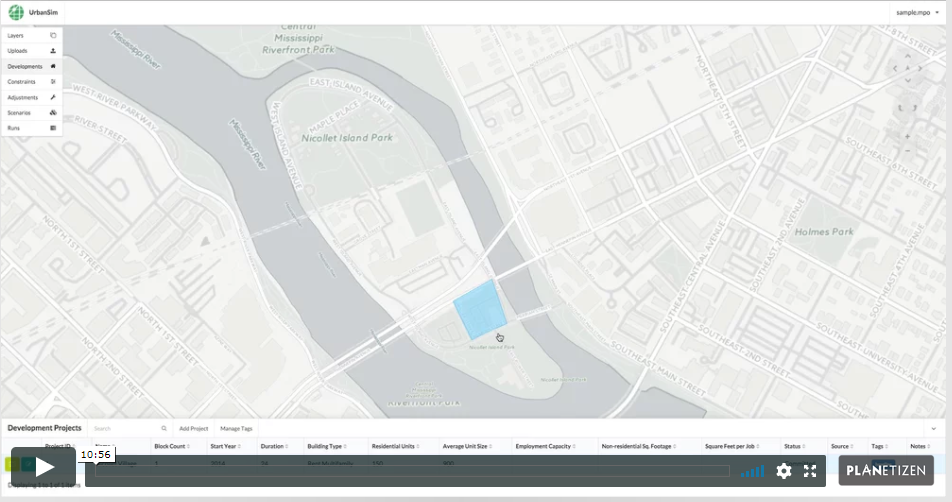
9. Development Projects, Development Constraints, and Model Adjustments (11 min)
Learn how to create and edit spatial scenario inputs, including known upcoming real estate development projects, real estate development constraints (e.g., zoning and land use regulations), and model adjustments.
10. Composing Scenarios and Running Simulations (6 min)
Learn how to compose complex scenarios, launch simulations, view indicators, and download results.
Course 2: Regional Planning Workflows in the UrbanSim Cloud Platform¶
Total time: 58 min
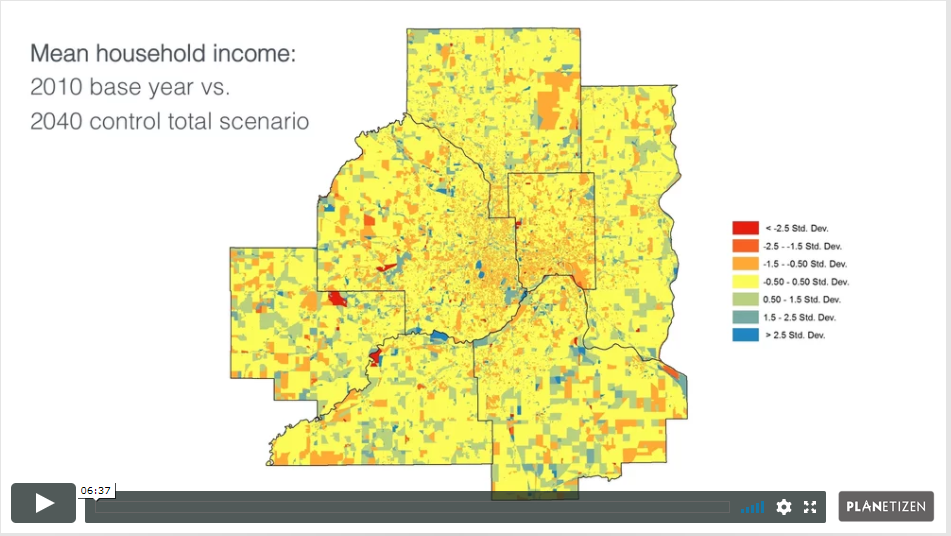
At the end of this course, participants will understand the basic land use forecasting workflows that can be completed using UrbanCanvas, as illustrated by a set of case studies. In this course, we use the platform to complete forecast-related workflows related to tracking and inserting development projects, inputting development constraint information, composing scenarios, evaluating simulation results, and comparing differences between scenarios and over time. Examples in this course will be drawn from the Minneapolis-St. Paul region, and participants are encouraged to follow along with a trial instance of the platform.
1. Introduction (3 min)
Introduction to the course.
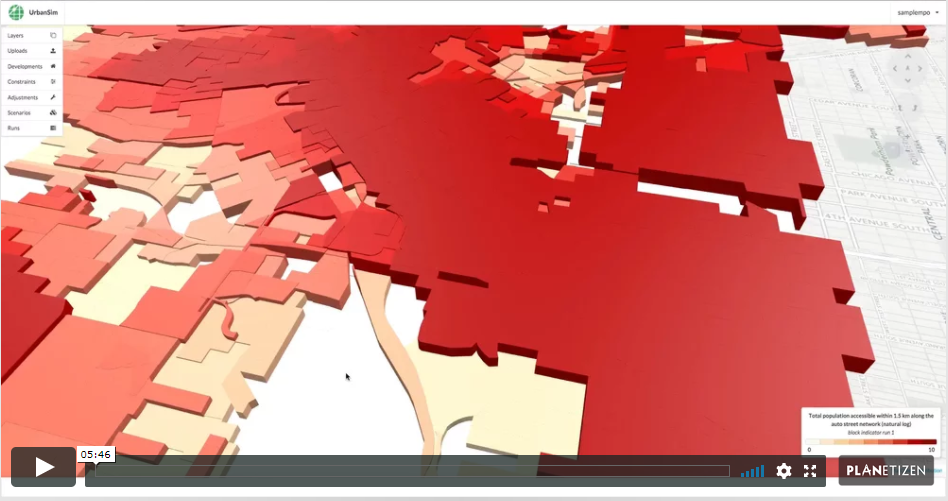
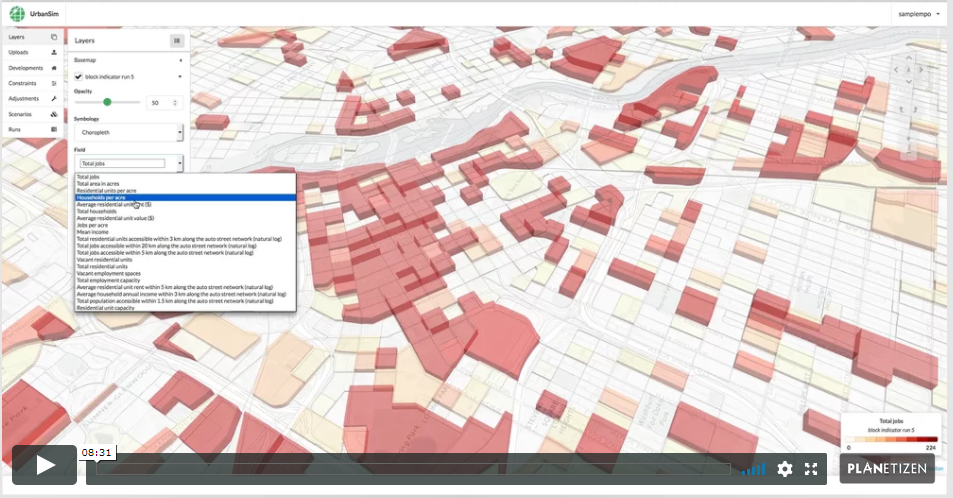
2. Initial Simulation and View Indicators (9 min)
UrbanCanvas gives Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) in the United States the ability to immediately start simulating their region using UrbanSim. This chapter demonstrates how to launch a simulation in the user interface right “out of the box” and view indicators generated by that simulation. Indicators are sets of useful variables exported at block, block group, tract, and TAZ level for each simulation. These indicators can be visualized on the map and themed based on any of a standard set of variables.
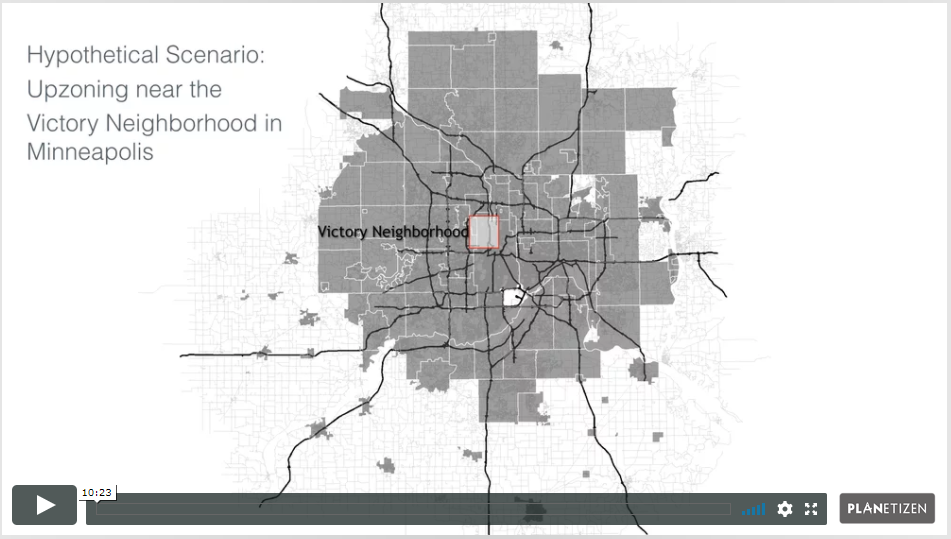
3. Alternative Land Use Regulations (11 min)
UrbanCanvas can be used to analyze the impact of land use regulations. Scenarios can be composed with different land use policies in place. The scenarios can be simulated, and then the results can be compared to see how alternative policies influence the spatial pattern of urban growth. This chapter describes how to use the platform to evaluate the impact of regulatory actions such as upzonings near transit or development restrictions in environmentally sensitive areas.
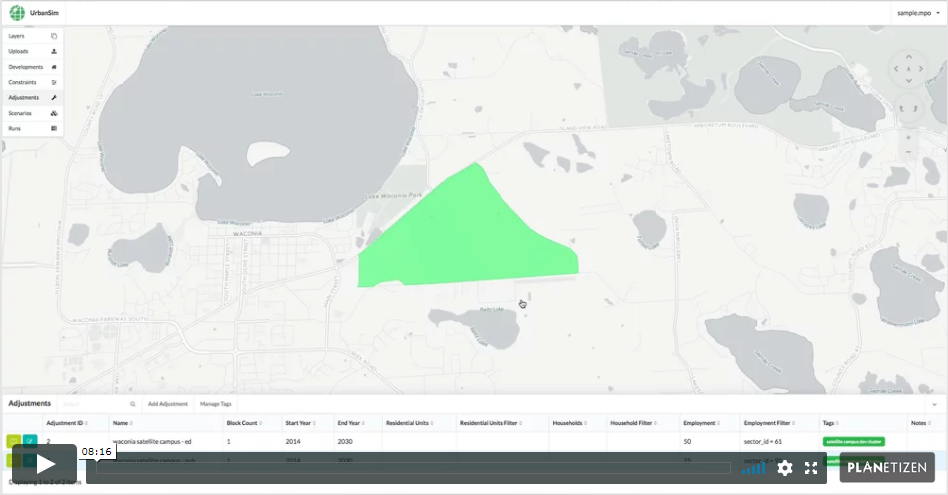
4. New Development Clusters (9 min)
Urban analysts sometimes need to assess the impact of major new development, for example the emergence of an employment subcenter or the establishment of a new university campus. New concentrations of activity can facilitate local agglomeration economies and spur the clustering of future growth. This chapter gives an overview of how to use UrbanCanvas to model the impact of major new developments, which can be incorporated into a baseline scenario or alternative scenarios.
5. Alternative Transportation Infrastructure (10 min)
One of the primary purposes of UrbanSim is to assist in the evaluation of transportation infrastructure projects. The model is sensitive to accessibility, so when new infrastructure alters accessibility patterns, predicted patterns of growth are influenced. This chapter discusses how to construct scenarios related to changes in transportation infrastructure and how to use the platform to gauge potential impact.
6. Alternative Macro Assumptions (7 min)
UrbanCanvas can be used to assess the spatial impact of alternative assumptions about future regional growth. For example, a scenario can be defined assuming rapid regional growth, or a separate scenario can be defined assuming tepid regional growth. Region-level conditions can also be specified in detail. For example, aggregate demographic or employment characteristics can be applied in scenarios. This chapter guides the user in modeling the impact of alternative macro assumptions and discusses the input tables and uploaders that help achieve this end.
7. Incorporating Local Feedback (11 min)
The platform aims to make it straightforward to incorporate local expertise and community feedback into a land use forecast. This chapter surveys the ways users can incorporate local feedback into the platform using the developments, constraints, and adjustments features.